Clusters¶
Overview¶
The Infrastructure > Clusters section is where the list of existing HVM clusters can be viewed. Here you can view high-level statistics about all clusters under management by VM Essentials manager, such as aggregate resource usage by all clusters and the number of workloads running across all of them. Click into an existing HVM cluster to view additional metrics such as hosts, VMs, resource utilization by the host, and a lot more.
Requirements¶
VM Essentials Role permission
Infrastructure: Clusters > Fullrequired for Viewing, Creating, Editing and Deleting ClustersVM Essentials Role permission
Infrastructure: Clusters > Readrequired for Viewing Cluster list and detail pages
Cluster Permissions¶
- Cluster Permissions
Each Cluster has Group and Service Plan access permissions settings (Gear icon > Permissions from the Clusters list page)
HVM clusters¶
An HVM cluster is a hypervisor clustering technology utilizing KVM. Beginning with just a few basic Ubuntu boxes, VM Essentials can create a cluster of HVM hypervisor hosts complete with monitoring, failover, easy migration of workloads across the cluster, and zero-downtime maintenance access to hypervisor host nodes. All of this is backed by a highly-granular RBAC engine, and image library with automation stacks.
Features¶
Host Features
Automated HVM cluster provisioning
CEPH storage configuration for multi-node clusters
CEPH summary, a high-level dashboard of CEPH components and status
DRS, automatic rebalancing of clusters based on resource consumption
Compatibility validation of network and storage devices at time of cluster provisioning
Hypervisor console
Configuration and deployment of OVS networks (VLANs)
Cluster and individual host monitoring
Add hosts to existing clusters
Console support for cluster hosts
Add, edit and remove networks and datastores from clusters
Gracefully take hosts out of service with maintenance mode
Migration of workloads across hosts
Configurable automatic failover of running workloads when a host is lost
Ability to add and provision to fibre channel storage resources or iSCSI storage resources via GFS2 filesystem
Governance through VM Essentials RBAC
Pass host-attached NVME, USB, and GPU hardware through to VMs running on the host
VM Features
Workload provisioning and monitoring (Linux or Windows workloads)
Console support for running workloads
Affinity placement, pin VMs to hosts
Brownfield discovery of existing VMs
Reconfigure VM sizing
Disk migration across datastores
UEFI support
Migration of VMs across hosts
Configure automatic failover for individual VMs in the event a host is lost
Reconfigure running workloads to resize plan, add/remove disks, and add/remove network interfaces
Backup and restore VM workloads, with optional synthetic full backups
Clone VMs
Take snapshots and revert to snapshots
VM Essentials library and automation support
Claim and consume host-attached NVME, USB, and GPU hardware to run hardware-accelerated workloads on VMs
Base Cluster Details¶
An HVM cluster using the hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) Layout consists of at least three hosts. Physical hosts are recommended to experience full performance of the solution. In smaller environments, it is possible to create an HVM cluster with three nested virtual machines, a single physical host (non-HCI only), or a single nested virtual machine (non-HCI only) though performance may be reduced. With just one host it won’t be possible to migrate workloads between hosts or take advantage of automatic failover. Currently, the default cluster layout requires hosts be a pre-existing Ubuntu 24.04 box with environment and host system requirements described in this section. An earlier cluster layout requiring Ubuntu 22.04 is also included. VM Essentials handles cluster configuration by providing the IP address(es) for your host(s) and a few other details. Details on adding the cluster to VM Essentials are contained in the next section.
Hardware Requirements
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04 (for the latest cluster layout version, prior versions for HVM hosts running Ubuntu 22.04 are also available)
CPU: One or more 64-bit x86 CPUs, 1.5 GHz minimum with Intel VT or AMD-V enabled
Memory: 4 GB minimum. For non-converged Layouts, configure HVM hosts to use shared external storage, such as an NFS share or iSCSI target. Converged Layouts utilize Ceph for clustered storage and require a 4 GB minimum memory per Ceph disk
Disk Space: For converged storage, a data disk of at least 500 GB is required for testing. More storage will be needed for production clusters. An operating system disk of 15 GB is also required. Clusters utilizing non-converged Layouts can configure external storage (NFS, etc.) while VM Essentials will configure Ceph for multi-node clusters
Network Connectivity: HVM hosts must be assigned static IP addresses. They also need DNS resolution of the VM Essentials appliance and Internet access in order to download and install system packages for dependencies, such as KVM, Open vSwitch (OVS), and more
Note
Ubuntu 22.04 uses netplan for networking and it is the responsibility of the customer to establish recommended networking configurations prior to provisioning an HVM cluster. To configure a static IP address, change into the directory holding the config files (cd /etc/netplan) and edit the existing configuration file (/etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml or /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml or /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml). If desired, backup the existing configuration prior to editing it (cp /etc/netplan/<file-name>.yaml /etc/netplan/<file-name>.yaml.bak). For additional information on configuration file formatting, refer to netplan documentation. Once the configuration is updated, validate and apply it (netplan try). The try command will validate the configuration and apply it if it’s valid. If invalid, it will automatically be rolled back.
Note
Clustered storage needs as much network bandwidth as possible. Network interfaces of at least 10 Gbps with jumbo frames enabled are required for clustered storage and for situations when all traffic is running through the management interface (when no compute or storage interface is configured). It’s highly likely that performance will be unacceptable with any lower configurations.
Description |
Source |
Destination |
Port |
Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
VM Essentials Agent communication with the VM Essentials appliance |
HVM host |
VM Essentials appliance server |
443 |
TCP |
HVM host configuration and management |
VM Essentials appliance server |
HVM host |
22 |
TCP |
Inter-host communication for clustered deployments |
HVM host |
HVM host |
22 |
TCP |
VM Essentials server SSH access for deployed virtual machines |
VM Essentials appliance server |
Hosted virtual machines |
22 |
TCP |
VM Essentials server WinRM (HTTP) access for deployed virtual machines |
VM Essentials appliance server |
Hosted virtual machines |
5985 |
TCP |
VM Essentials server WinRM (HTTPS) access for deployed virtual machines |
VM Essentials appliance server |
Hosted virtual machines |
5986 |
TCP |
Ceph Storage |
HVM host |
HVM host |
3300 |
TCP |
Ceph Storage |
HVM host |
HVM host |
6789 |
TCP |
Ceph MDS/OSD |
HVM host |
HVM host |
6800-7300 |
TCP |
Example Cluster Deployment
In this example cluster, each host box consists of:
4 vCPU
16 GB memory
20 GB OS boot disk
250 GB data disk (deployed to
/dev/sdb)3 network interfaces for management, storage, and compute traffic (set to
eth0,eth1, andeth2, respectively, in this example. Your environment may differ.)
Note
250 GB data disks used in this example are simply for demonstration purposes. A typical test cluster should consist of at least 500 GB storage and more will be required for production. Do not raid disks on physical servers. Currently, only one data disk may be used, which is given in the DATA DEVICE configuration during cluster setup. In the very near future, an update will be provided to allow multiple data disks to be used. These will be added to the total Ceph storage in one large volume. Until that update, only one data disk may be given in the configuration.
HVM clusters must also live in Private Cloud-type Clouds (See Infrastructure > Clouds). A pre-existing Cloud may be used or a new Cloud could be created to house HVM clusters.
Provisioning the Cluster¶
As mentioned in the previous section, HVM hosts should be running Ubuntu 24.04 to use the latest HVM cluster layout (version 1.2+). HVM hosts running Ubuntu 22.04 can also be used (select HVM cluster layout 1.1). I also have a Private Cloud-type Cloud to house the cluster. Begin the cluster creation process from the Clusters list page (Infrastructure > Clusters). Click + ADD CLUSTER and select “HVM”.
VM Essentials gives the option to select a hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) LAYOUT or non-HCI. In this example, the HCI Layout is used (requires a three-node minimum). Next, configure the names and IP addresses for the host boxes (SSH HOST). The SSH HOST name configuration is simply a display name in VM Essentials, it does not need to be a hostname. By default, configuration space is given for three hosts which is what this example cluster will have. You must at least configure one and it’s possible to add more by clicking the (+) button. The SSH PORT is pre-configured for port 22, change this value if applicable in your environment. Next, set a pre-existing user on the host boxes (SSH USERNAME and SSH PASSWORD) and SSH KEY. Use a regular user with sudo access.
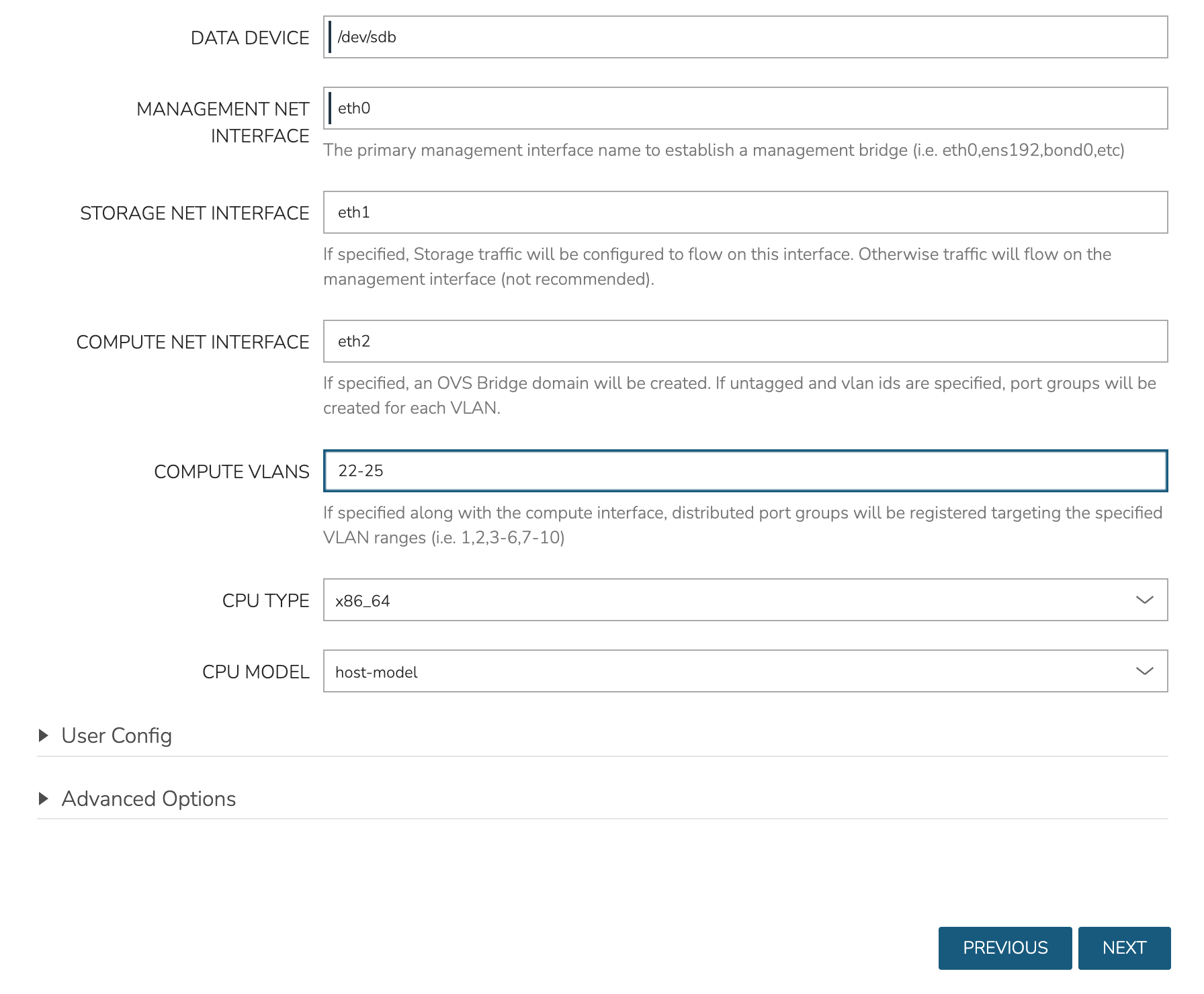
In the next part of the modal, you’ll configure the storage devices and network interfaces. When Ceph initializes, it needs to be pointed to an initial data device. Configure this in the DATA DEVICE field. At this time, only one device may be given but in the near future, an update will allow for multiple devices to be configured which would be added to the total Ceph storage as one large volume. Find your disk name, if needed, with the lsblk command. In my case, the target device is located at /dev/sdb.
Though not strictly required, it’s recommended to have separate network interfaces to handle cluster management, storage traffic, and compute. In this example case, eth0 is configured as the MANAGEMENT NET INTERFACE which handles communication between the cluster hosts. eth1 is configured as the STORAGE NET INTERFACE and eth2 is configured as the COMPUTE NET INTERFACE. The COMPUTE VLANS field can take a single value (ex. 1) or a range of values (ex. 22-25). This will create OVS port group(s) selectable as networks when provisioning workloads to the cluster. If needed, you can find your network interface names with the ip a command.
Finally, only one CPU TYPE is currently supported (x86_64) though this may change in the future. For CPU MODEL configuration, we surface the entire database of model configurations from libvirt. If unsure or if you don’t know of a specific reason to choose one or the other, select host-passthrough which is the default option.
At this point we’ve kicked off the process for configuring the cluster nodes. Drill into the Cluster detail page and click on the History tab. Here we can monitor the progress of configuring the cluster. VM Essentials will run scripts to install KVM, install Ceph, install OVS, and to prepare the cluster. In just a short time, the cluster provisioning should complete and the cluster will be ready to deploy workloads.
Provisioning a Workload¶
At this point, the cluster is ready for workloads to be provisioned to it. Within the Instance provisioning wizard (See Provisioning > Instances documentation for more details on provisioning), there is now the “HVM” Instance Type. This Instance will allow you to choose from any HVM cluster-compatible images within your environment. Out of the box, VM Essentials does not include any compatible images but there is a section later in this guide covering the process of onboarding existing QCOW images into the UI as Virtual Images and another section covering the process of prepping Windows images from the downloaded ISO.
After arriving at the Configure tab of the provisioning wizard, select a Plan based on resource needs. From the RESOURCE POOL field, select the desired HVM cluster. When configuring VOLUMES for the new workload, note that space can be claimed from the Ceph volume. Within NETWORKS, we can add the new workload to one of the VLANS set up as part of cluster creation. Finally, note that we can choose the HOST the workload should run on in addition to selecting the compatible image.
Review and complete the provisioning wizard. After a short time, the workload should be up and running. With a workload now running on the cluster, we can take a look at some of the monitoring, migration, failover, and other actions we can take for workloads running on HVM clusters.
Note
HVM clusters support CPU pinning (tying specific vCPUs associated with running workloads to specific physical CPU cores). Currently, this must be done manually by accessing the appropriate HVM host and issuing virsh commands or editing XML. Adding UI tools to view and control CPU pinning is on the product roadmap to be added in the near future. Despite the requirement to edit CPU pinning manually, this is a supported action for workloads running on HVM clusters.
Monitoring the Cluster¶
With the server provisioned and a workload running, take a look at the monitoring and actions capabilities on the cluster detail page (Infrastructure > Clusters, then click on the new HVM cluster). View cluster performance and resource usage (Summary and Monitoring tabs), drill into individual hosts (Hosts tab), see individual workloads (VMs tab), and more.
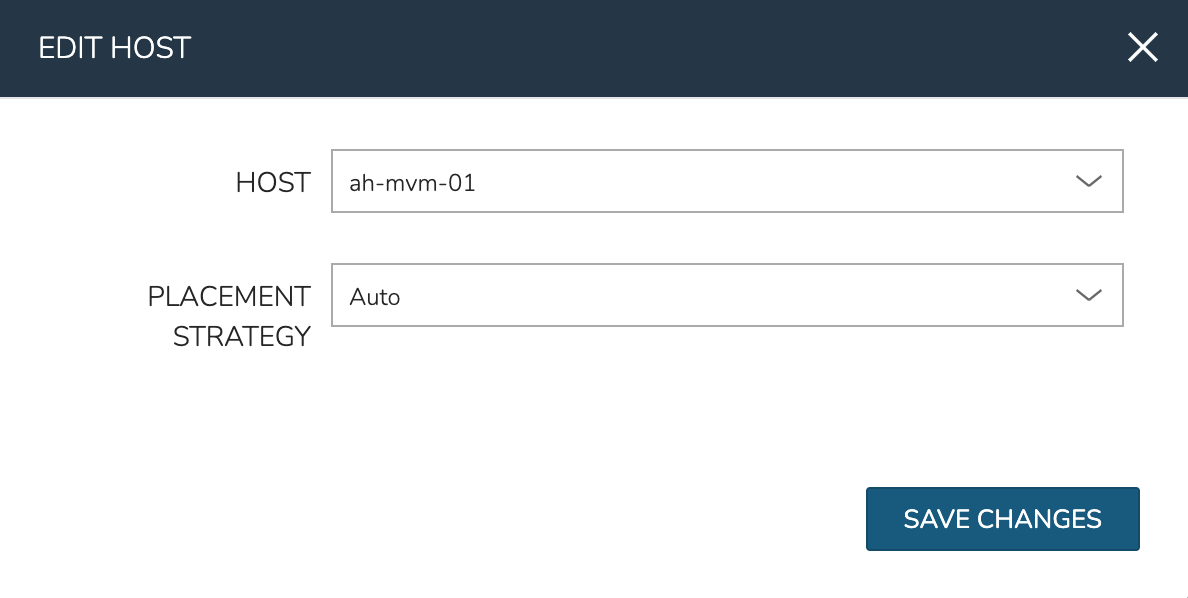
Moving Workloads Between Hosts
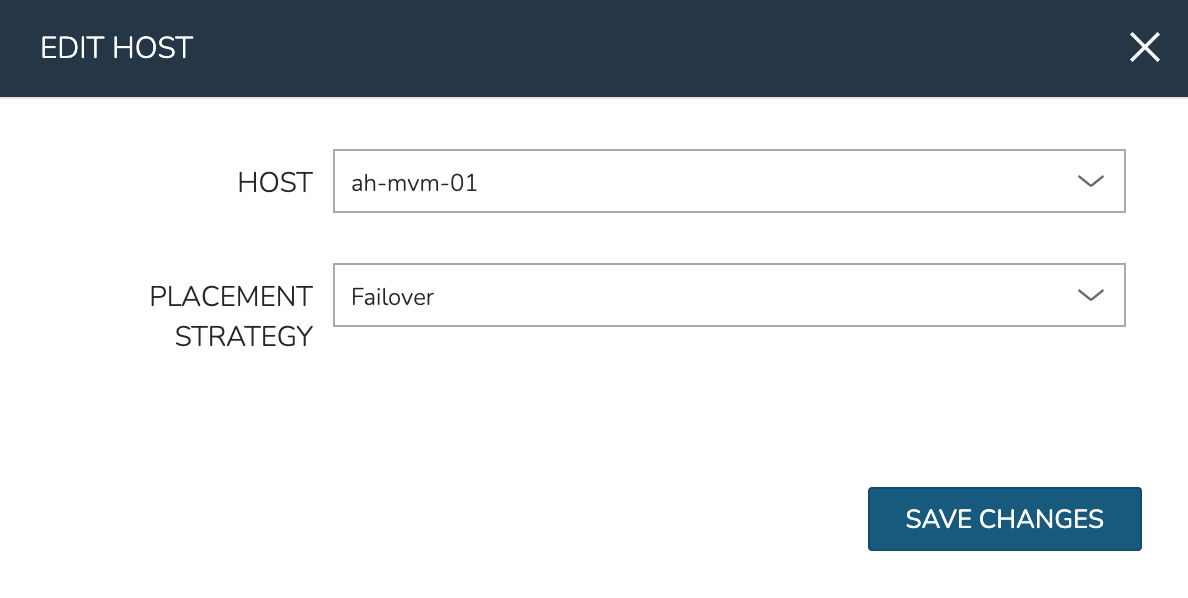
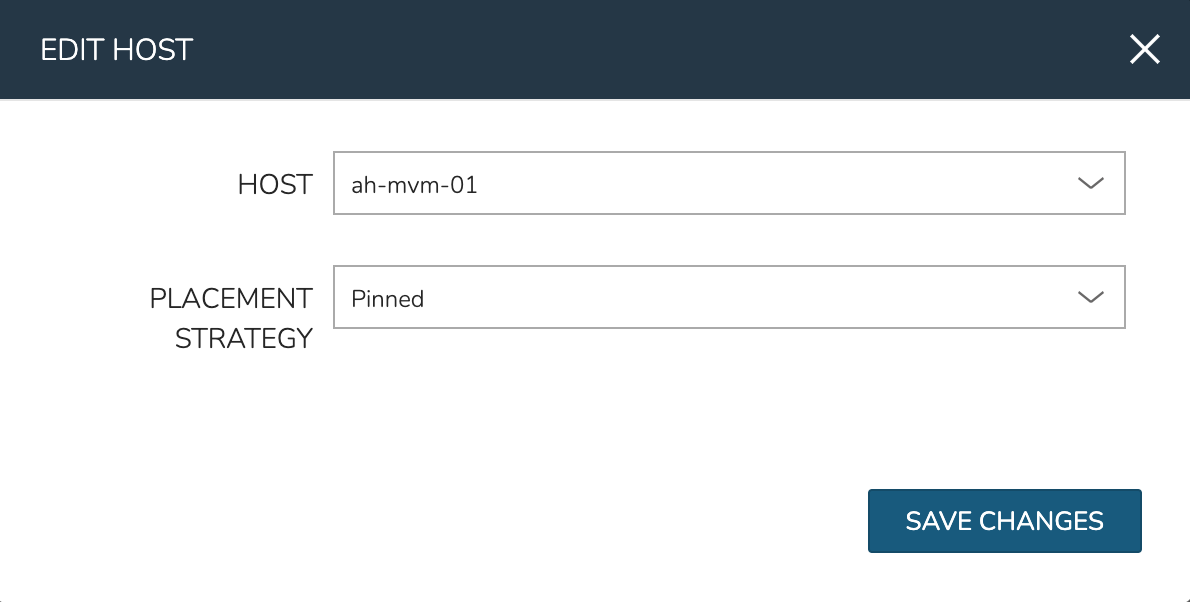
To manually move workloads between hosts, drill into the detail page for the VM (from the VMs tab of the cluster detail page). Click ACTIONS and select “Manage Placement”. Choose a different host and select from the following placement strategies:
Auto: Manages VM placement based on load
Failover: Moves VMs only when failover is necessary
Pinned: Will not move this workload from the selected host
Within a short time, the workload is moved to the new host.
Adding hosts
The process of adding hosts to a pre-existing cluster is very similar to the process of provisioning the cluster initially. The requirements for the new worker node will be identical to the nodes initially added when the cluster was first provisioned. See the earlier sections in this guide for additional details on configuring the worker nodes.
To add the host, begin from the Cluster detail page (selected from the list at Infrastructure > Clusters). From the Cluster detail page, click ACTIONS and select “Add Worker”. Configurations required are the same as those given when the cluster was first created. Refer to the section above on “Provisioning the Cluster” for a detailed description of each configuration.
Once VM Essentials has completed its configuration scripts and joined the new worker node to the cluster, it will appear in a ready state within the Hosts tab of the Cluster detail page. When provisioning workloads to this Cluster in the future, the new node will be selectable as a target host for new Instances. It will also be an available target for managing placement of existing VMs running on the cluster.
Note
It’s useful to confirm all scripts related to creating the new host and joining the new host to the cluster completed successfully. To confirm, navigate to the detail page for the new host (Infrastructure > Clusters > Selected Cluster > Hosts Tab > Selected Host) and click on the History tab. Confirm all scripts, even those run on the pre-existing hosts, completed successfully as it’s possible the new host was added successfully (green status) but failed in joining the cluster. When such a situation occurs it may appear adding the new host was successful though it will not be possible to provision workloads onto it due to not joining the cluster successfully.
Maintenance Mode
HVM hosts can be easily taken out of service for maintenance when needed. From the host detail page, click ACTIONS and then click “Enter Maintenance.” When entering maintenance mode, the host will be removed from the pool. Live VMs that can be migrated will be moved to new hosts. VMs that are powered off will also be moved when possible. When a live VM cannot be moved (such as if it’s “pinned” to the host), the host will not go into maintenance mode until that situation is cleared. You could manually move a VM to a new host or you could power it down if it’s non-essential. After taking that action, attempt to put the host into maintenance mode once again. VM Essentials UI provides a helpful dialog which shows you which VMs live on the host are to be moved as the host goes into maintenance mode. When maintenance has finished, go back to the ACTIONS menu and select “Leave Maintenance.”
Failover
HVM clusters support automatic failover of running workloads in the event of the loss of a host. Administrators can control the failover behavior through the “Manage Placement” action on any running VM. From the VM detail page, click ACTIONS and select “Manage Placement”. Any VM with a placement strategy of “Auto” or “Failover” will be eligible for an automatic move in the event its host is lost. When the loss of a host does occur, the workload will be up and running from a different cluster host within just a short time if it’s configured to be moved during an automatic failover event. Any VMs pinned to a lost host will not be moved and will not be accessible if the host is lost. When the host is restored, those VMs will be in a stopped state and may be restarted if needed.

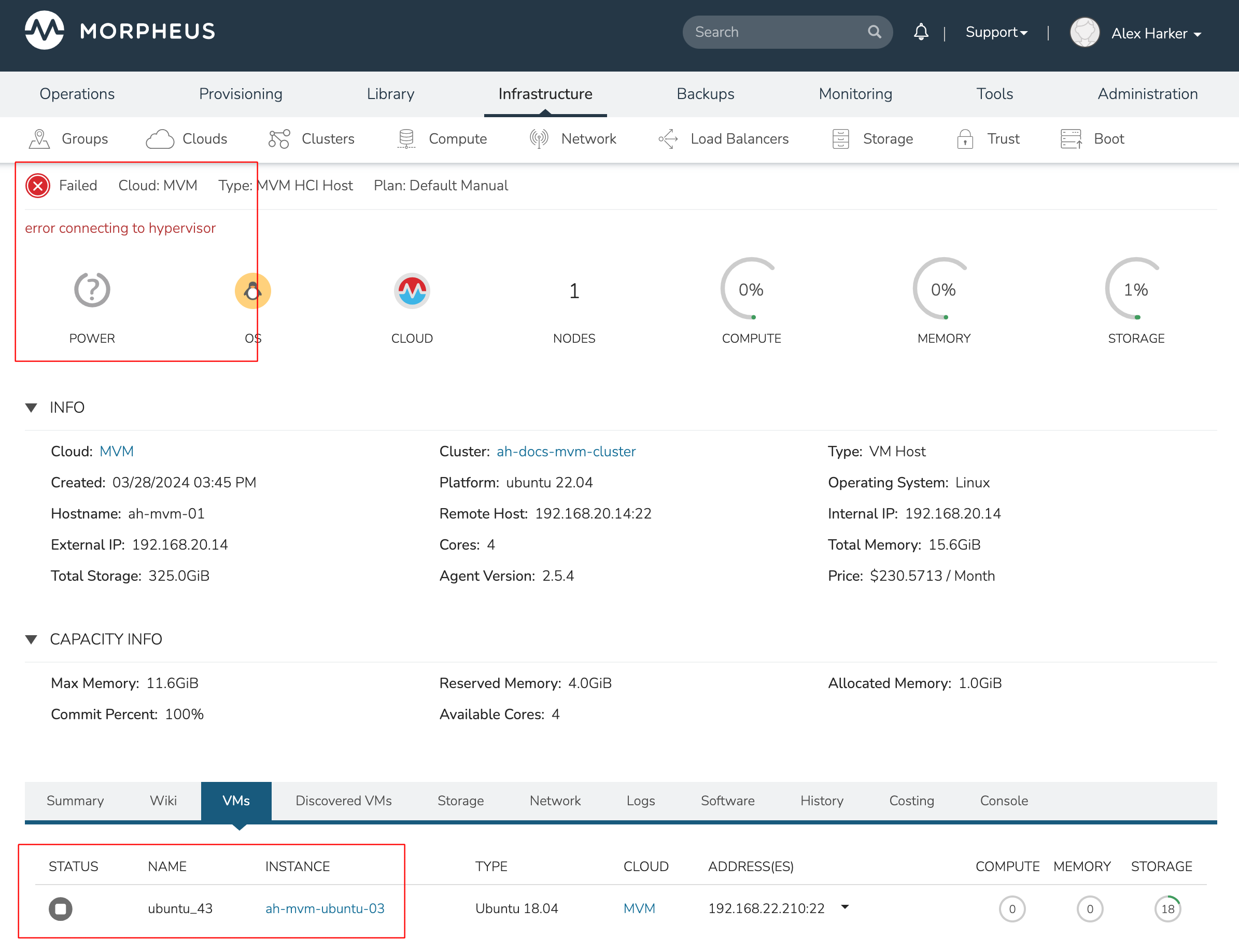
Each of these VMs is configured for a different failover strategy. When the host is lost, we should expect to see the first two VMs moved to an available host (since they have the “Auto” and “Failover” placement strategies, respectively). We should not see the third VM moved.
After loss of the host these three VMs were running on, we can see the lost host still has one associated VM in a stopped state. The other two VMs are running on a second host which is still available.
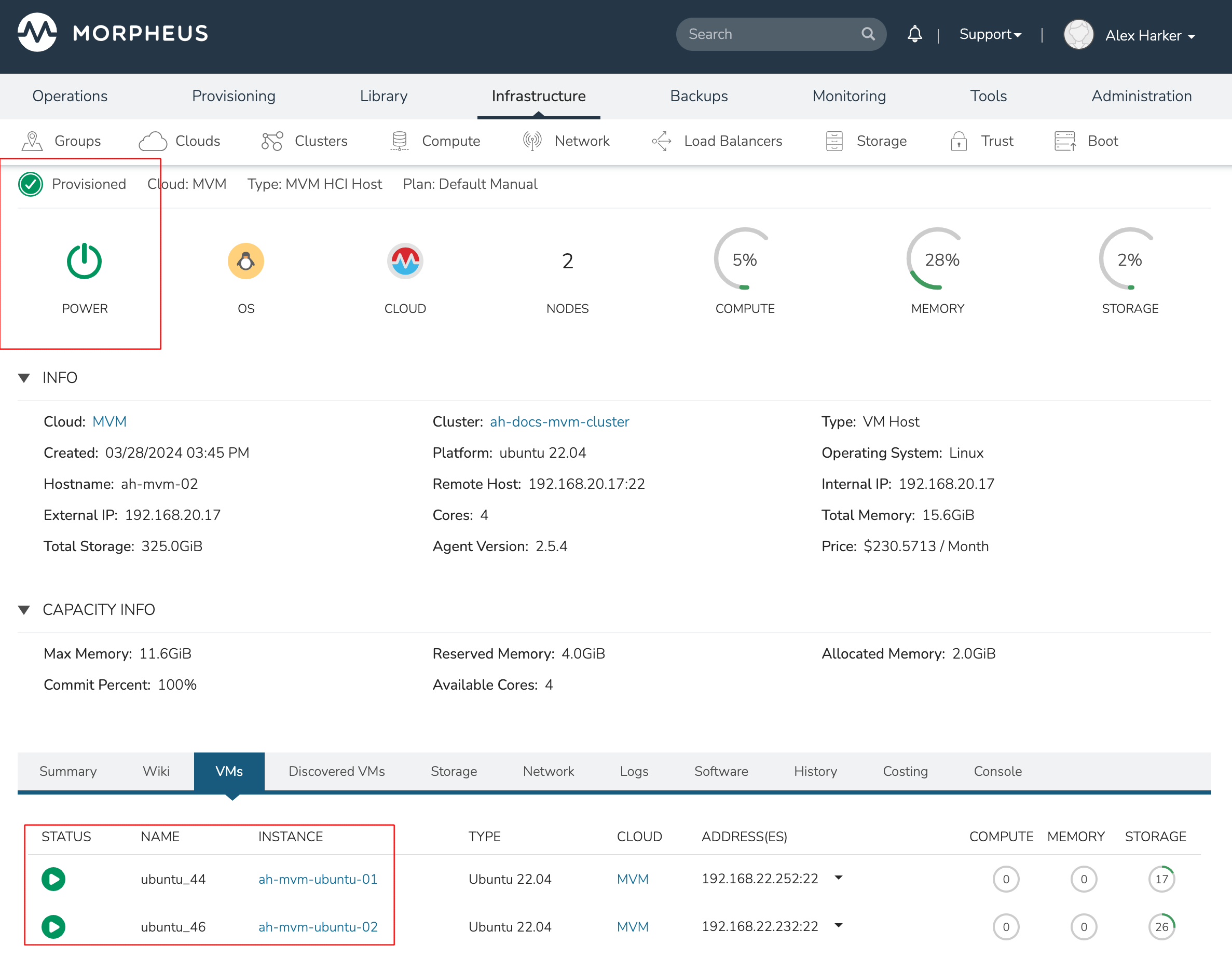
When the lost host returns, the moved VMs will come back to their original host. The third VM is associated with this host as well and is in a stopped state until it is manually restarted.
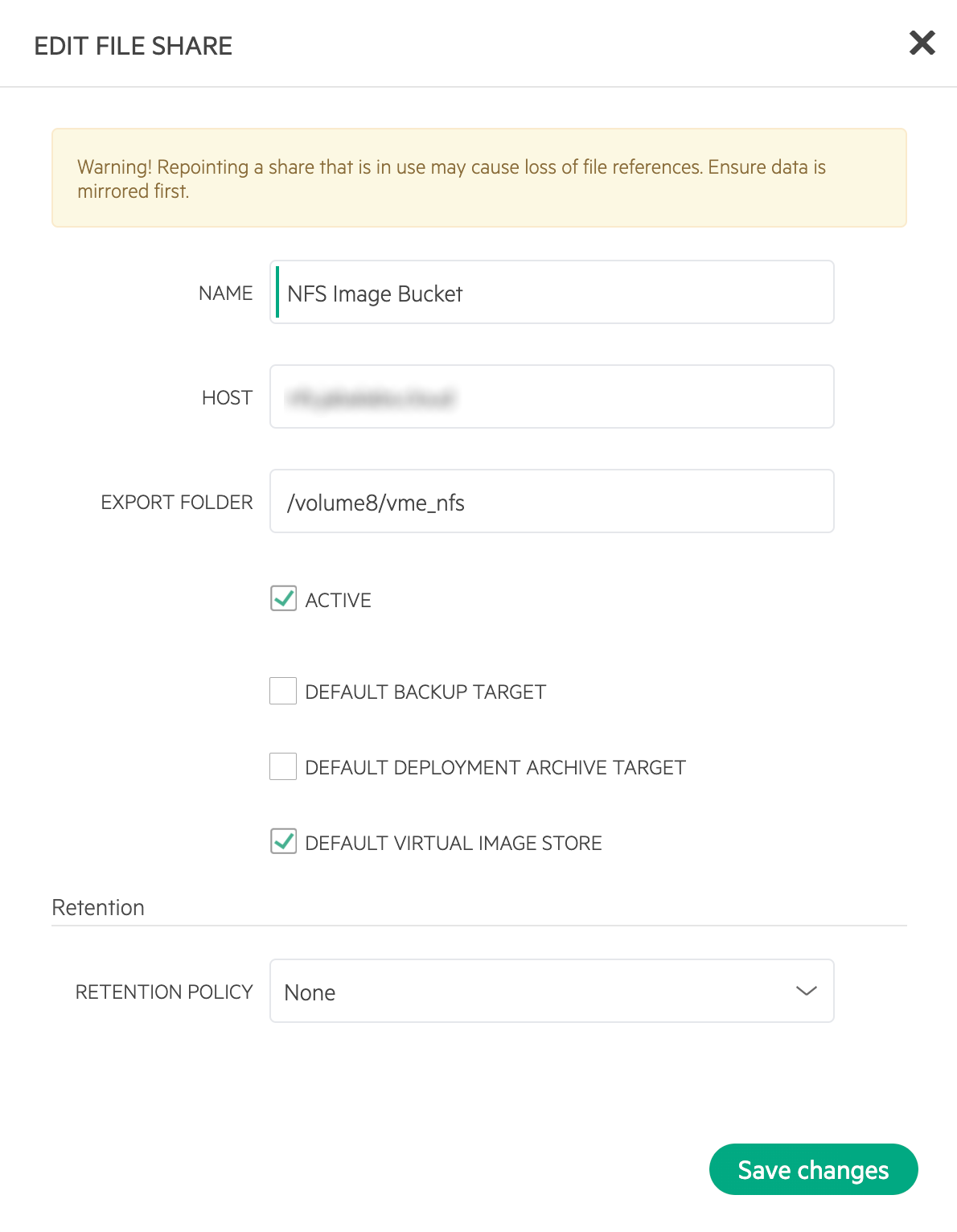
Adding an NFS Datastore
Existing NFS shares can be used with HVM clusters for virtual machine storage. These are added and viewed from the Storage tab of the cluster detail page and, once added and active, become selectable as targets for virtual machine storage.
Note
Ensure NFS is properly configured to allow all of the HVM hosts to access the shared directory, including permissions to read and write. For backup purposes, it’s also helpful to give VM Essentials access to NFS.
Start by navigating to the Storage tab of the cluster detail page. Make sure the Data Stores subtab is also selected. Here you will see a list of existing datastores with some additional information, such as type, capacity, and status. Click ADD. Enter the NAME for the datastore in VM Essentials and select the TYPE as NFS Pool. Note that the datastore name cannot be changed once it has been created. This will update the available fields to include the additional fields needed to integrate the NFS server. Enter the SOURCE HOST which is the hostname or the IP address of the NFS server. Finally, enter the SOURCE DIRECTORY which is the directory path of the NFS share. Click SAVE.
Once the modal is saved, it will take a few minutes to initialize the new datastore and show a successful online status in VM Essentials. Once this initialization process is completed, the datastore can now be used as VM storage for cluster.
Image Prep (Windows)¶
This section will go through the steps to prepare a Windows image which can be successfully provisioned to HVM clusters. Additionally, this image can serve as a template from which additional images and VM Essentials Library items can be built. In this example case, we’ll start from downloading a Windows Server 2019 ISO directly from the Microsoft download center and go all the way through to creating a new Instance Type in VM Essentials that users can provision on-demand.
With the Windows ISO already downloaded, begin by uploading the ISO as a Virtual Image in VM Essentials. Virtual Images are added in Library > Virtual Images. Click + ADD and then choose “ISO.” Before adding the file itself, set the following configurations on the Virtual Image:
NAME: A name for the Virtual Image in VM Essentials, such as “Windows Server 2019 ISO”
OPERATING SYSTEM: “windows server 2019”
MINIMUM MEMORY: Filters out Service Plans at provision time which do not meet the minimum value. For this image type, I’ve set 4 GB
In addition to the above, there are a number of checkbox configurations here (many of them are in the expandable “Advanced” section), some of which are checked by default. They should all be unchecked except for “VIRTIO DRIVERS LOADED?” within the “Advanced” expandable section.
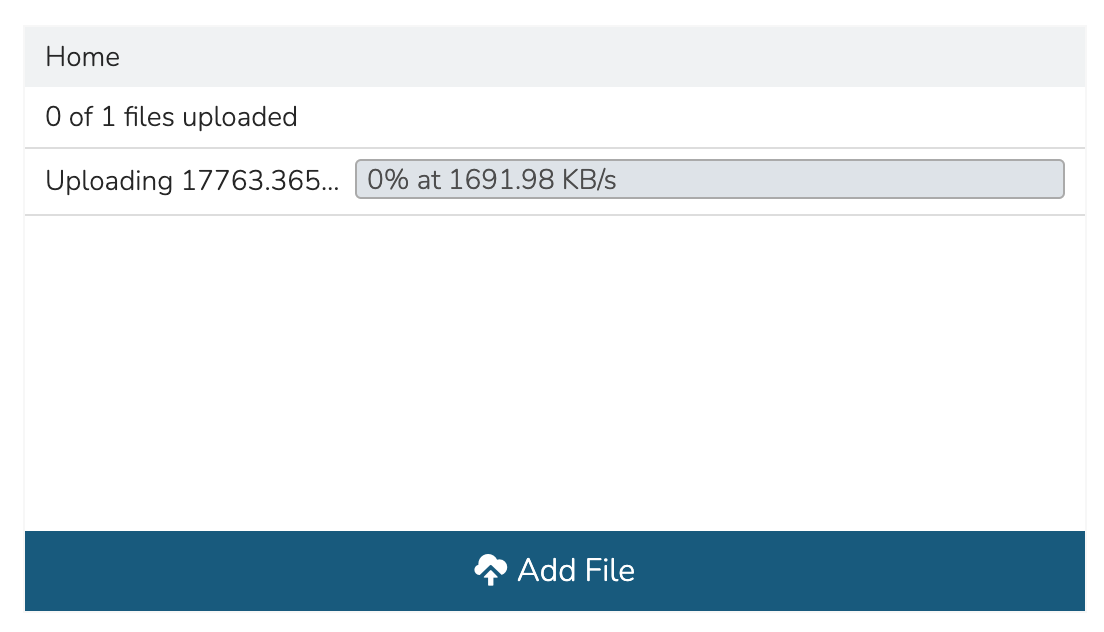
With the configurations set, it’s time to upload the ISO to VM Essentials. Keep in mind that if you do not specify a bucket in which the file should be uploaded, it will be uploaded to the appliance itself. If you choose to do this, be sure you have enough space to store the images you need. Within the UPLOAD VIRTUAL IMAGE modal is a large dropzone labeled “Drop Files Here.” You can drag and drop the ISO file here or you can click the button labeled “Add File” and browse for it. A progress bar will appear, wait until the file is completely uploaded before you save and dismiss the modal. After the file has completely uploaded, click SAVE CHANGES.
Next, we’ll provision a VM from the ISO using the built-in HVM Instance Type. Once running, we will configure the VM to any specific requirements and convert it to a template. Navigate to Provisioning > Instances and click + ADD. On the TYPE tab of the Instance provisioning wizard, we select the Instance Type to provision. In this case, select “HVM” and click NEXT.
On the GROUP tab, select the Group and Cloud containing the target MVM Cluster and provide a name for the new Instance. In my case, I have an automatic naming policy setting my Instance name, but depending on your appliance configuration you may need to enter a custom name. Click NEXT.
On the CONFIGURE tab, first select the IMAGE. Select the Windows server ISO that was uploaded in the previous step. Based on the minimum memory configuration that was set on the Virtual Image, Plans which are too small will be filtered out. Among compatible Plans, select one that meets your requirements. Next, set the RESOURCE POOL, which is the HVM cluster you’re targeting. Configure disks and disk sizes, as well as network details (this will vary based on HVM cluster configuration). Finally, select the HOST, which is the HVM host within the cluster that the new Instance should initially be provisioned onto.
As a final step, we need to also expand the “Advanced Options” section and make sure “ATTACH VIRTIO DRIVERS” is checked. This will attach an ISO containing the VirtIO drivers which we’ll use later. Click NEXT.
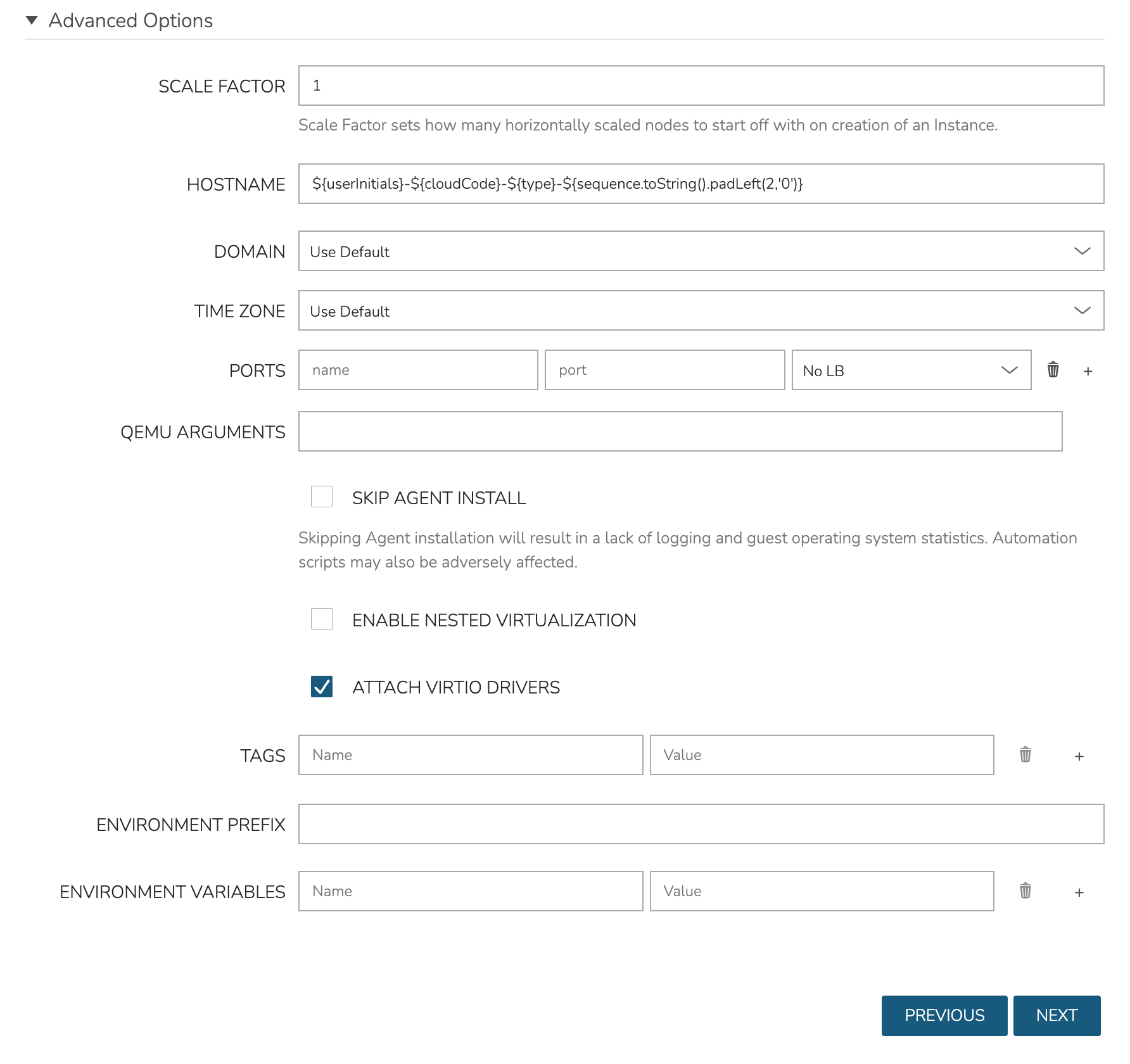
The final two tabs of the wizard, AUTOMATION and REVIEW, do not require any configuration changes though you may want to review the Instance settings on the final tab. When done, click COMPLETE.
Click on the newly provisioning Instance from the Instances list page. Since this image is being provisioned for the first time, the image must be uploaded to the HVM host. This can take a little bit of time but any future attempts to provision workloads from this image will skip this step. Wait for the Instance to fully complete and appear in a green “Ready” status.
Once the Instance has fully finished provisioning, launch a console session by clicking ACTIONS and then “Open Console.” This will open a new window with a console session into the VM.
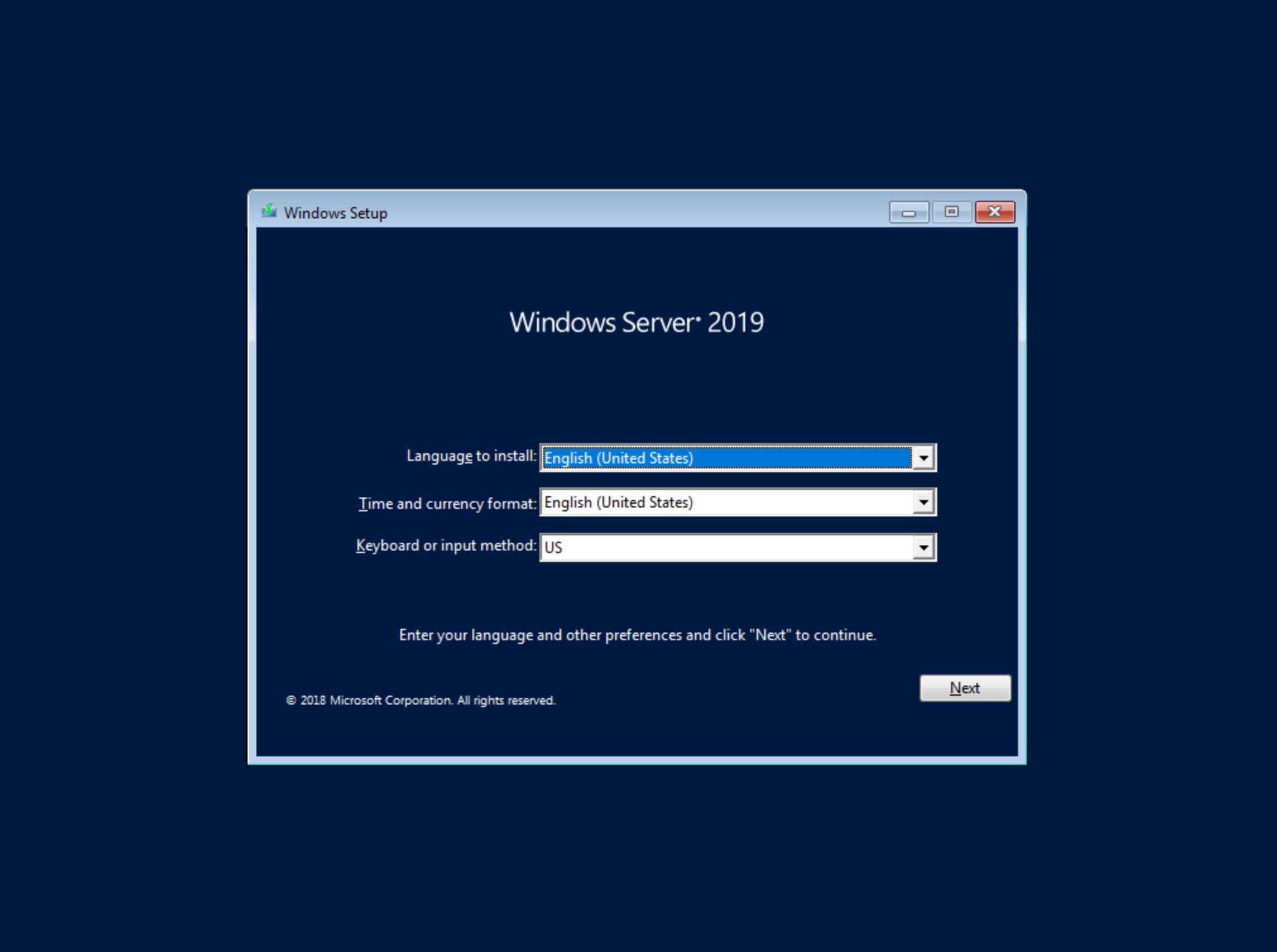
After selecting the language, click “Next.” On the following screen, click “Install Now.” This will begin the Windows setup process on our new VM. You’ll next select the operating system type you wish to install. For this example, I’m installing 2019 standard with desktop experience. Click “Next.”
Accept the licensing terms and click “Next.”
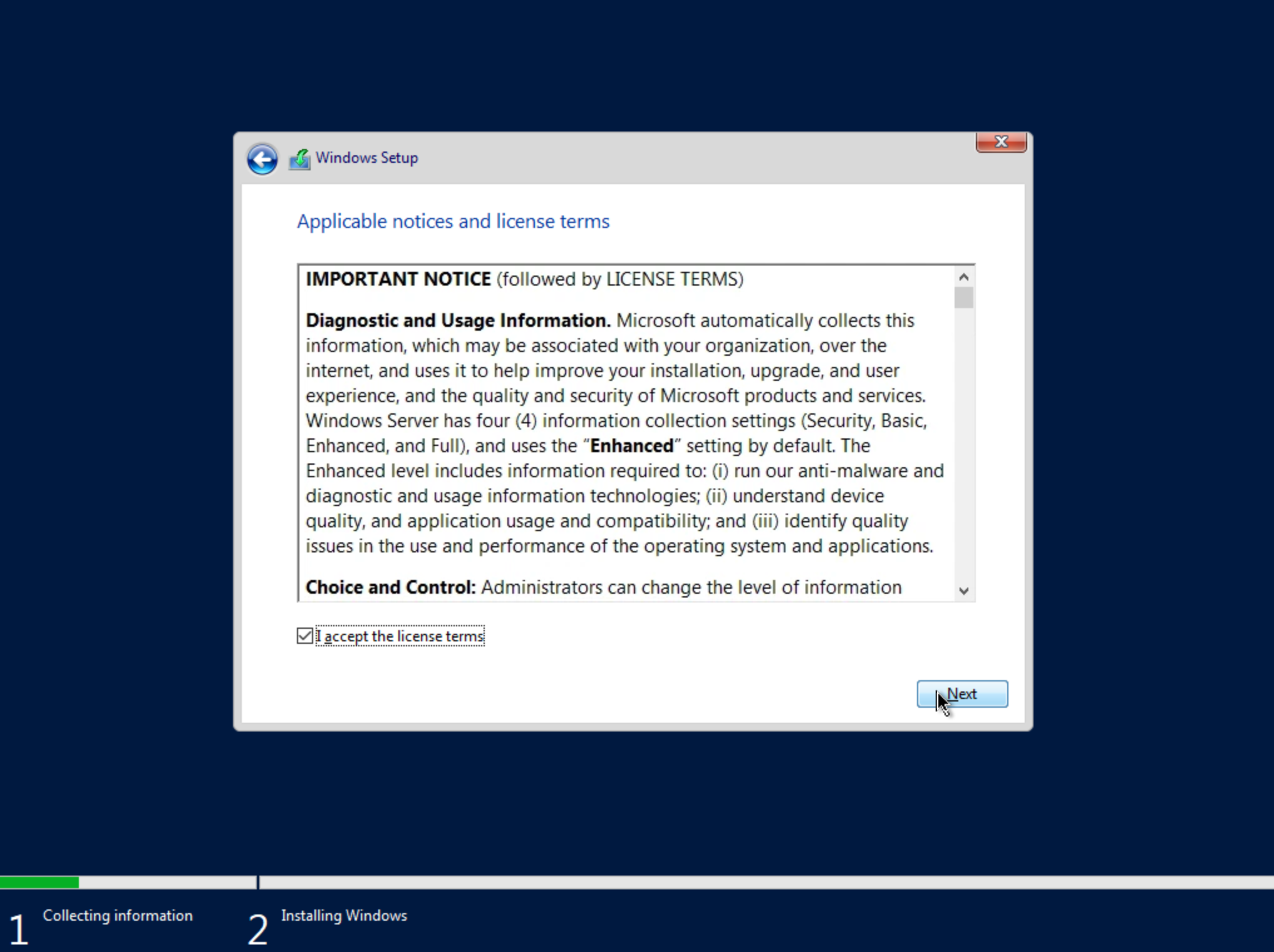
On the next screen, choose a custom install.
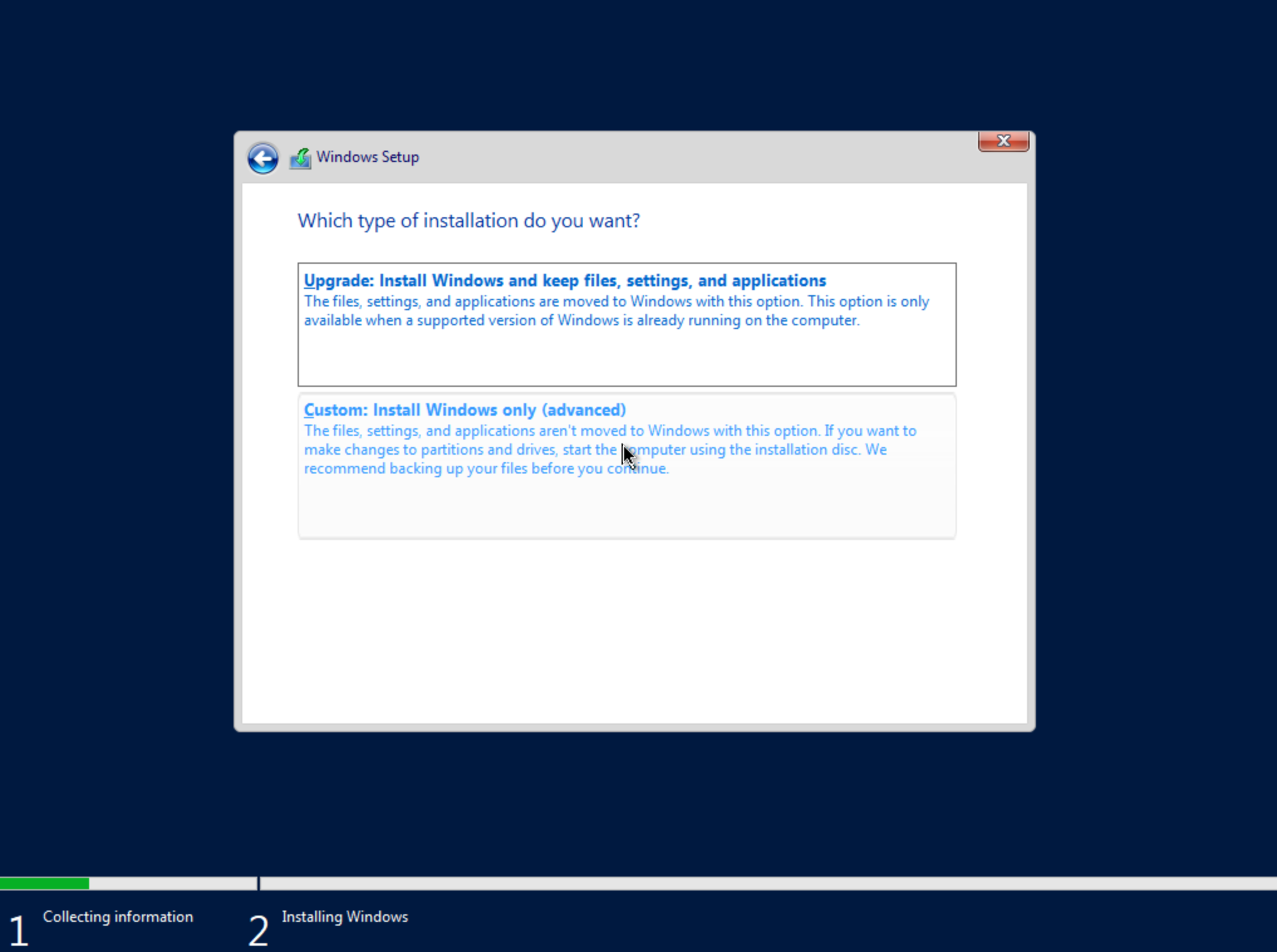
The next screen asks where Windows should be installed and may be empty. Click “Load Driver” to locate the mounted disk image containing the VirtIO drivers. The search should return a number of VirtIO SCSI controller packages for various Windows flavors. Select the proper package for the Windows version being installed. Click “Next.”
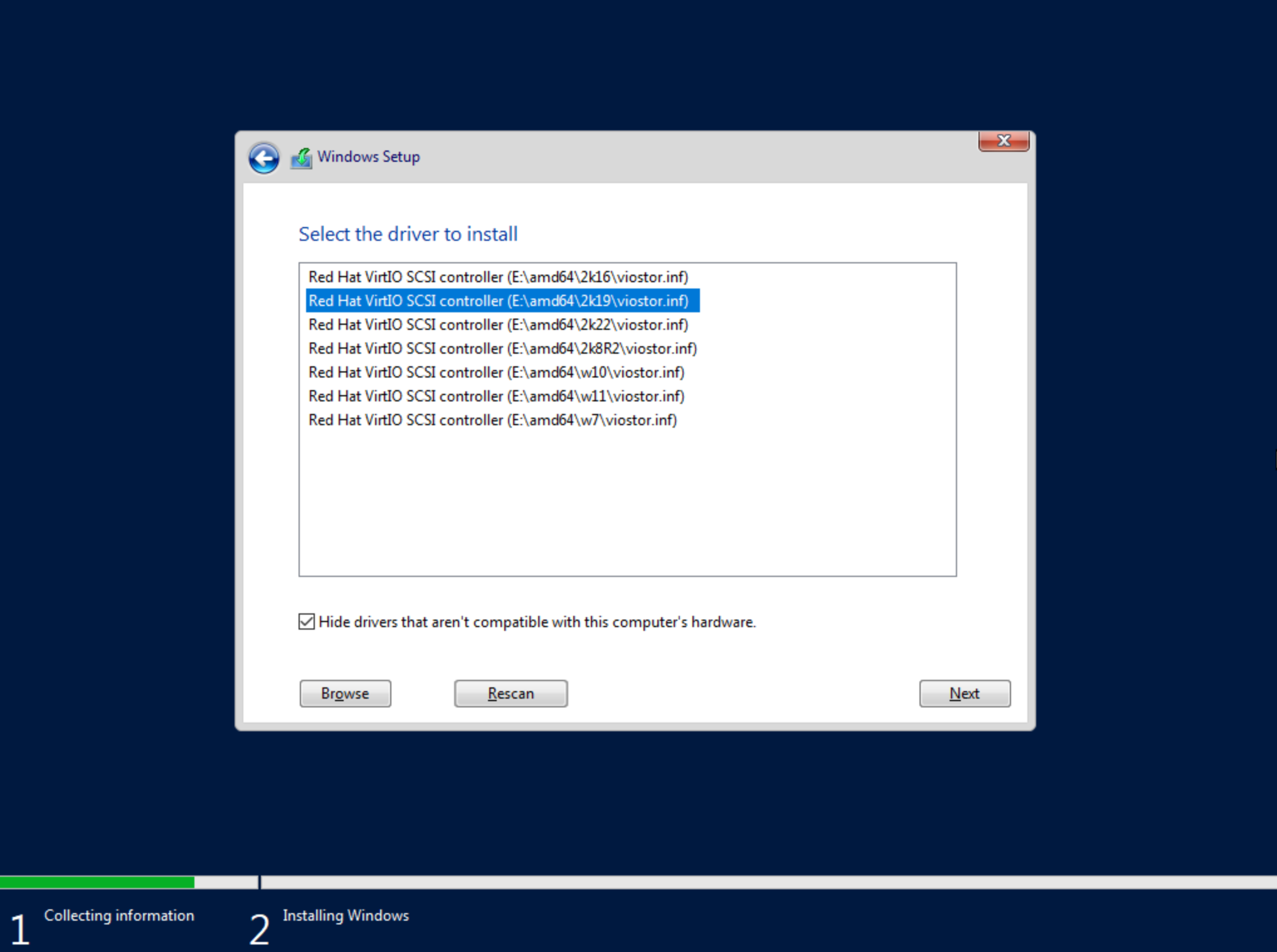
After a moment, we’re back at the screen asking where Windows should be installed. We should see the disk(s) of size and type selected at the time the VM was provisioned. Select the proper disk and click “Next.” The Windows installation will now begin. Once Windows has fully installed, proceed to the next step.
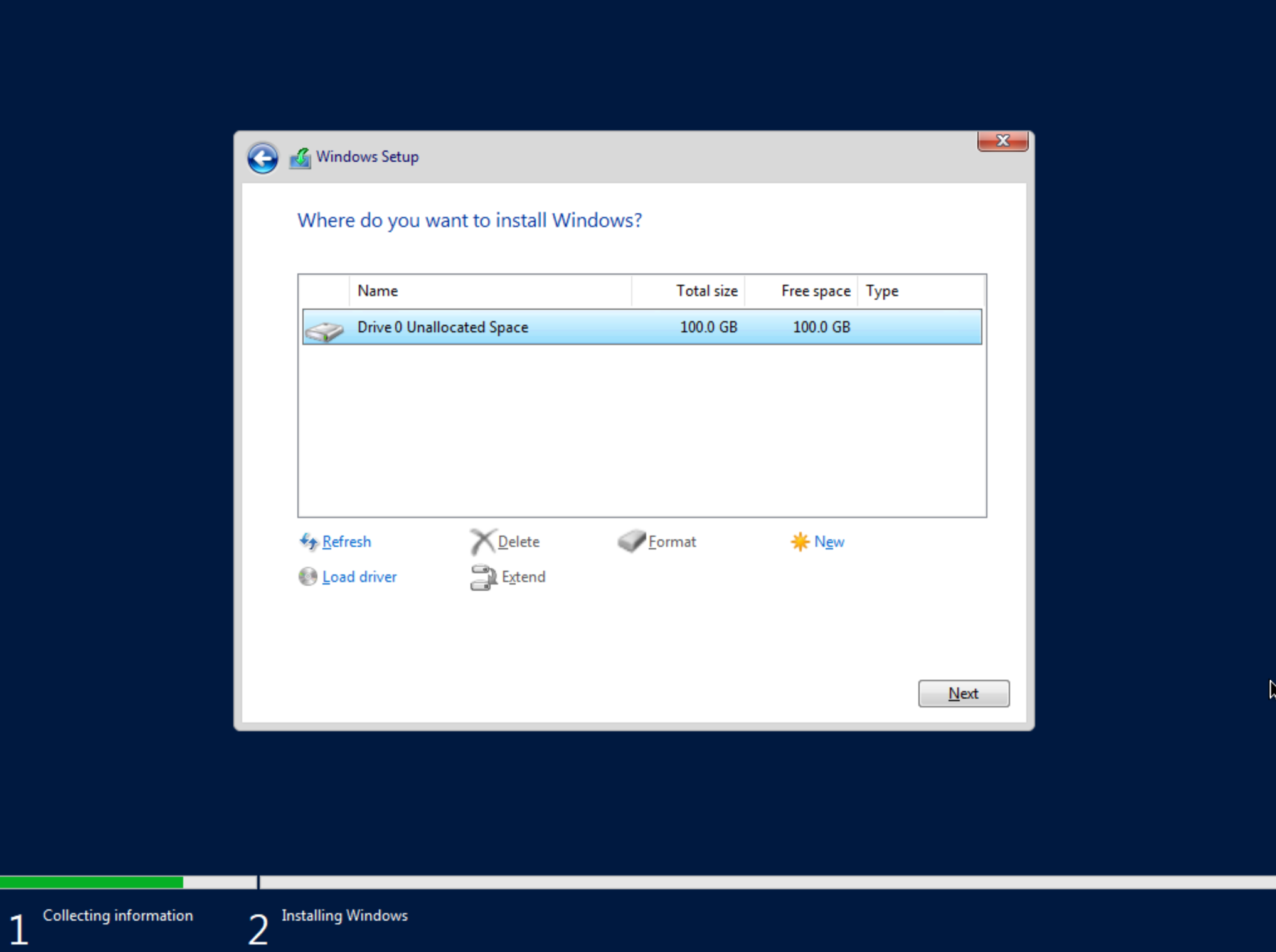
Following installation, Windows will restart and prompt for an Administrator user password. Set the password and log in as Administrator. Currently, there are no network interfaces configured. We need to install the VirtIO drivers to get this machine onto the network. We have a disk image mounted with the driver installer so we need to navigate to that drive and launch the installer. Open Windows Explorer and locate the drive in the side bar. In my case, it’s the E: drive. Right-click on virtio-win-guest-tools and select “Install.”
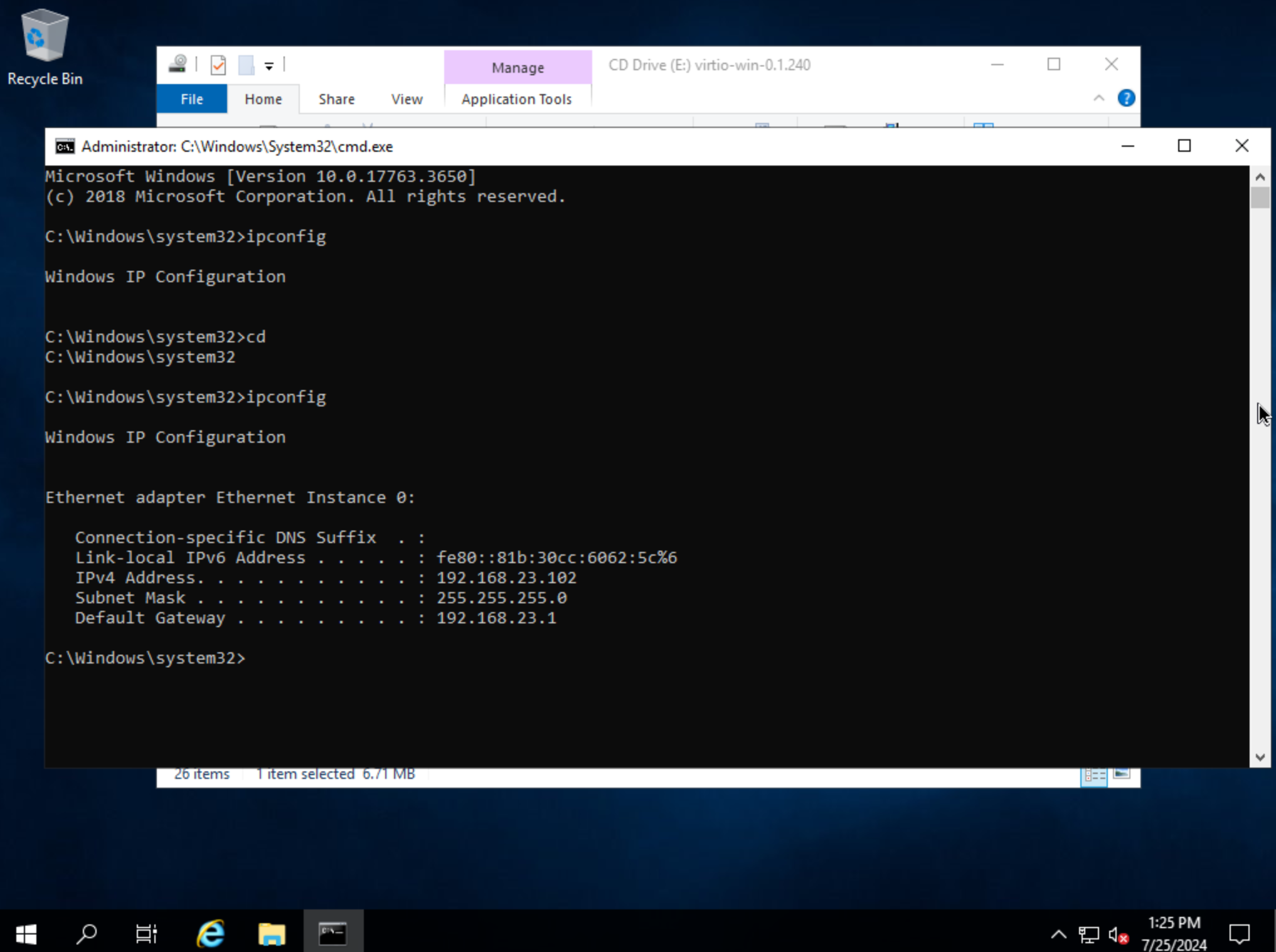
Step through the installer. Simply click “Next” or “Install” through each step, there are no configuration changes needed. Once the installer has completed, click “Finish.” You can confirm we now have a network interface by opening a Command Prompt session and using the ipconfig command. One network adapter should be listed.
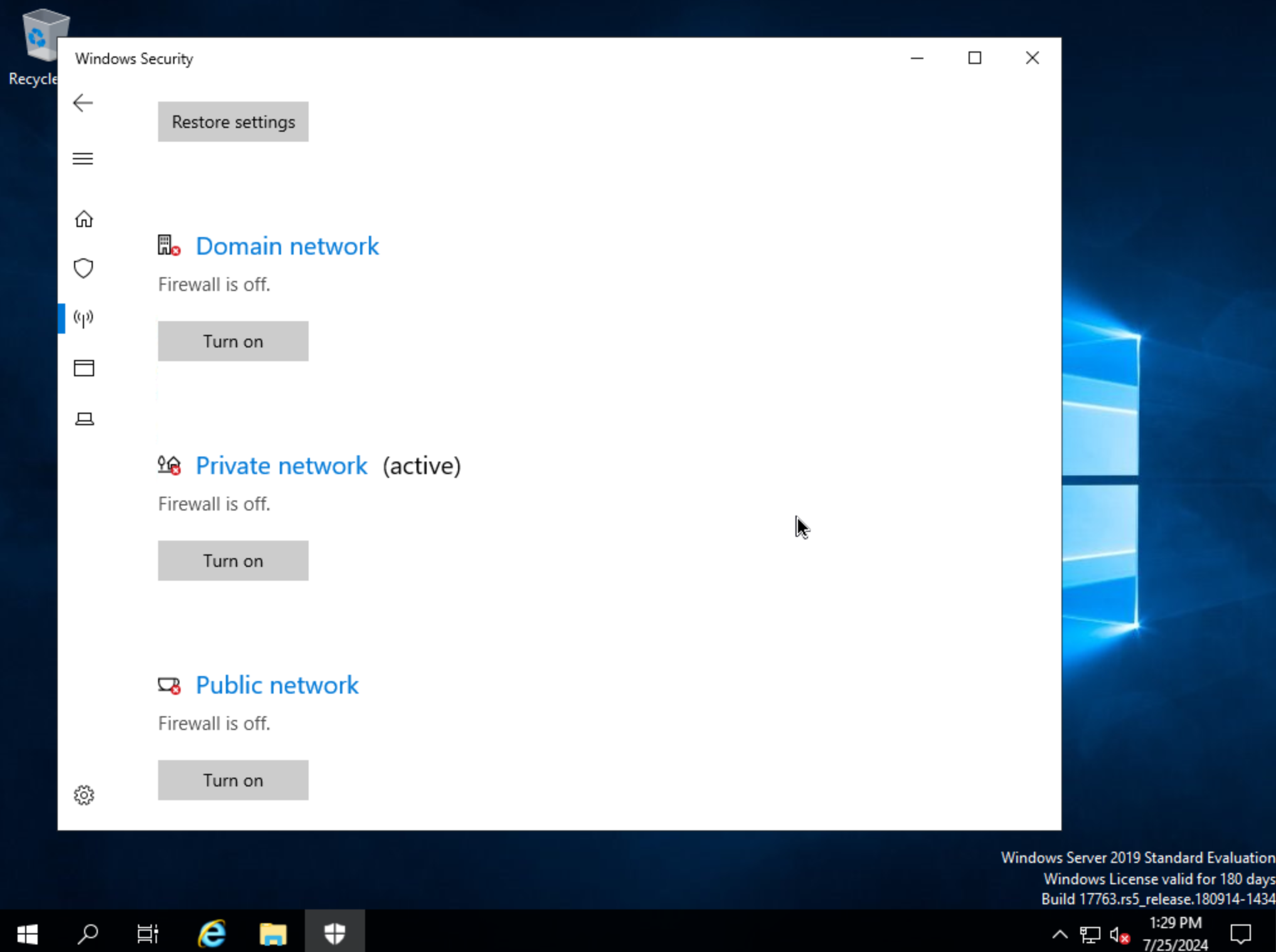
We can now eject the two virtual disks, drives D: and E: in my case. Then, launch Windows Security so we can disable firewalls. Turn off firewall for domain, private network, and public network.
Next, back in Command Prompt, run winrm quickconfig to configure winrm. Within Services, ensure that winrm (Windows Remote Management) is set to automatic on startup. Right-click on the Start button and select Run. Enter “sysprep” and click OK. In the Windows Explorer window that appears, right-click on sysprep and click “Run as Administrator”. Under “Shutdown Options”, choose Quit and click OK. If this is set to shutdown, VM Essentials will simply restart the VM. Once this is completed, a new file Sysprep_succeeded.tag appears in Windows Explorer.

We’re now done configuring Windows and the console window can be closed. We’ll move on to creating a template from the VM we just configured. Begin by opening an SSH session into the VM Essentials appliance server. Confirm jq is up to date on the appliance box (apt install jq). Then, go ahead and stop the running Windows VM. We can do this from the Instance detail page in VM Essentials. Click ACTIONS and then “Stop Server.” Still on the Instance detail page, click ACTIONS and then “Import as Image.” This will perform a snapshot and create a new Virtual Image (Library > Virtual Images).
The Virtual Image is not usable until it’s in an active status and the UI indication may display an active status even before it’s fully ready. If it’s “SAVING” or “QUEUED,” it is still being prepared and saved. To determine the current status of the Virtual Image, check with a call to VM Essentials API like the one below. When the return output lists a status of “Active,” the image is ready to be provisioned from.
curl -k --request GET --url https://xx.xx.xx.xx/api/virtual-images/<id>
--header 'accept: application/json' --header 'authorization: Bearer xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx' |
jq '.virtualImage.status'
Once saved, additional configurations are needed on the Virtual Image in VM Essentials. Edit the new Virtual Image and check the following configurations:
MINIMUM MEMORY: Set as appropriate
SYSPREPPED/GENERALIZED IMAGE?: Checked
INSTALL AGENT?: Checked
USERNAME: Remove if present
PASSWORD: Remove if present
VIRTIO DRIVERS LOADED?: Checked
All other checkbox-type configurations not mentioned in the above list should be unchecked. Click SAVE CHANGES.
At this point all image preparation steps are completed. Repeat the process of provisioning an HVM Instance Type selecting the new image in the future when needed.